Features of non-accidental injury (injury that should raise concerns) in a child in comparison to features suggestive of an accidental injury in a child
The assessment of any physical injury involves three stages:
- evaluating the injury itself, its extent, site and any particular patterns
- taking a history to understand how and why the injury occurred and whether the findings match the story given
- exploring the broader picture (e.g. the child's behaviour, the parent-child interaction, underlying risk factors or markers of emotional abuse or neglect)
Types of injury:
- bruising
- burns
- bite marks
- eye injuries
- bone fractures
- abrasions and lacerations
- intra-oral injuries
Typical features of accidental injuries
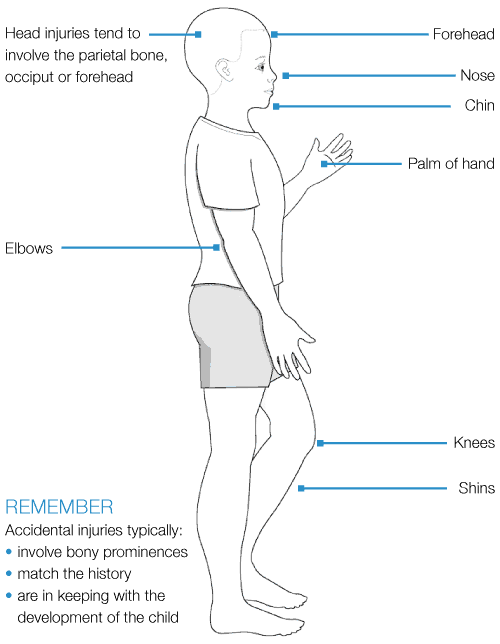
Typical features of non-accidental injuries (injuries that should raise concerns)
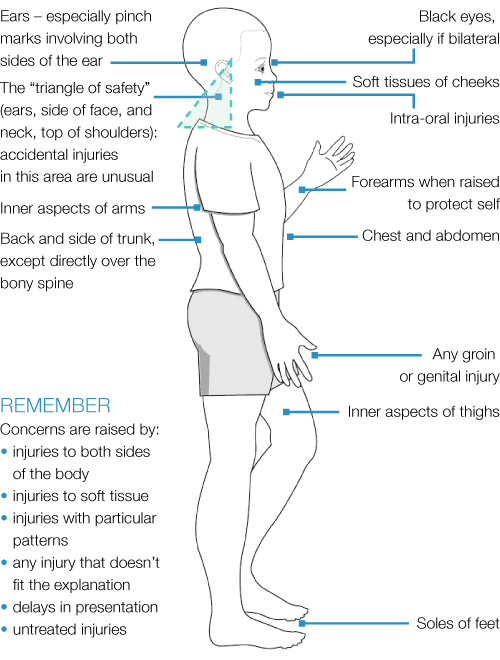
Figures reproduced with permission from Harris J, Sidebotham P, Welbury R et al. Child protection and the dental team: an introduction to safeguarding children in dental practice. COPDEND: Sheffield, 2006/2013, www.bda.org/childprotection
For detailed description of the types of non-accidental injuries then see
https://bda.org/childprotection/Recognising/Pages/Physical.aspx
Reference
- NICE. Child maltreatment: when to suspect maltreatment in under 18s. Clinical guideline CG89. Published July 2009, last updated October 2017
Related pages
Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.