Thrombocytopaenia
Thrombocytopaenia is a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood - it reduces the ability of the blood to clot and is thus a bleeding diathesis. It is defined as a platelet count less than 100 x 10^9/L (<100,000 per cubic mm).
In addition, it is important to consider also the causes of apparent thrombocytopaenia - i.e. conditions where there is platelet dysfunction.
Neonatal thrombocytopaenia has a modified differential diagnosis.
A suggested management of low platelet count in adults:
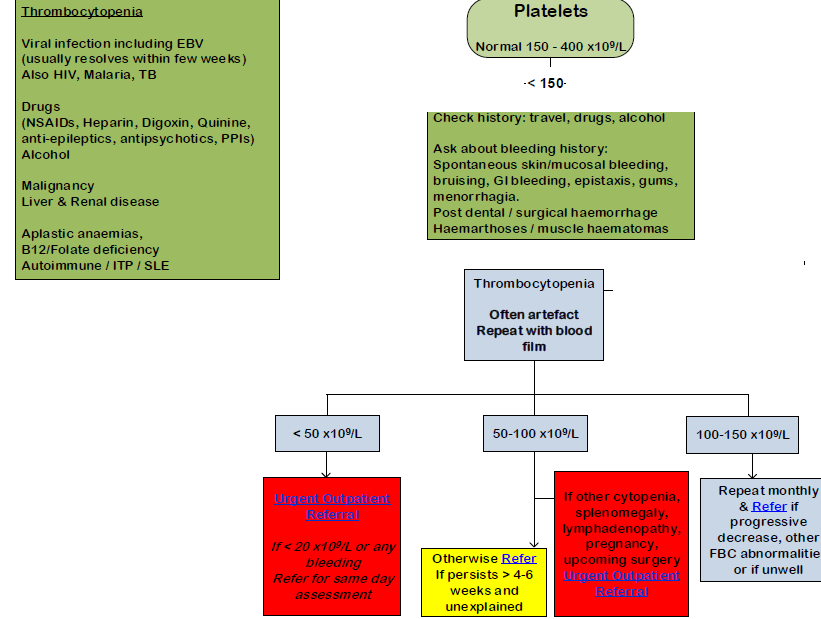
Reference:
- Provan D, Arnold DM, Bussel JB, et al. Updated international consensus report on the investigation and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2019 Nov 26;3(22):3780-817.
Related pages
- Aetiology
- Clinical features of a platelet disorder
- Investigations in primary care
- Neonatal thrombocytopaenia
- Platelet dysfunction
- Referral criteria from primary care - thrombocytopaenia (thrombocytopenia)
- Thrombocytopaenia in pregnancy
- NICE - indication for platelet transfusions if low platelets (thrombocytopaenia)
- Thrombocytosis
- Abnormal full blood count
Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.