Anterior approach - aspiration or injection of the knee joint
Anterior Approach to injection of the knee joint
Based on contributions from Dr Elspeth Wise and Dr Alan Walker on behalf of the Primary Care Rheumatology and Musculoskeletal Medicine Society
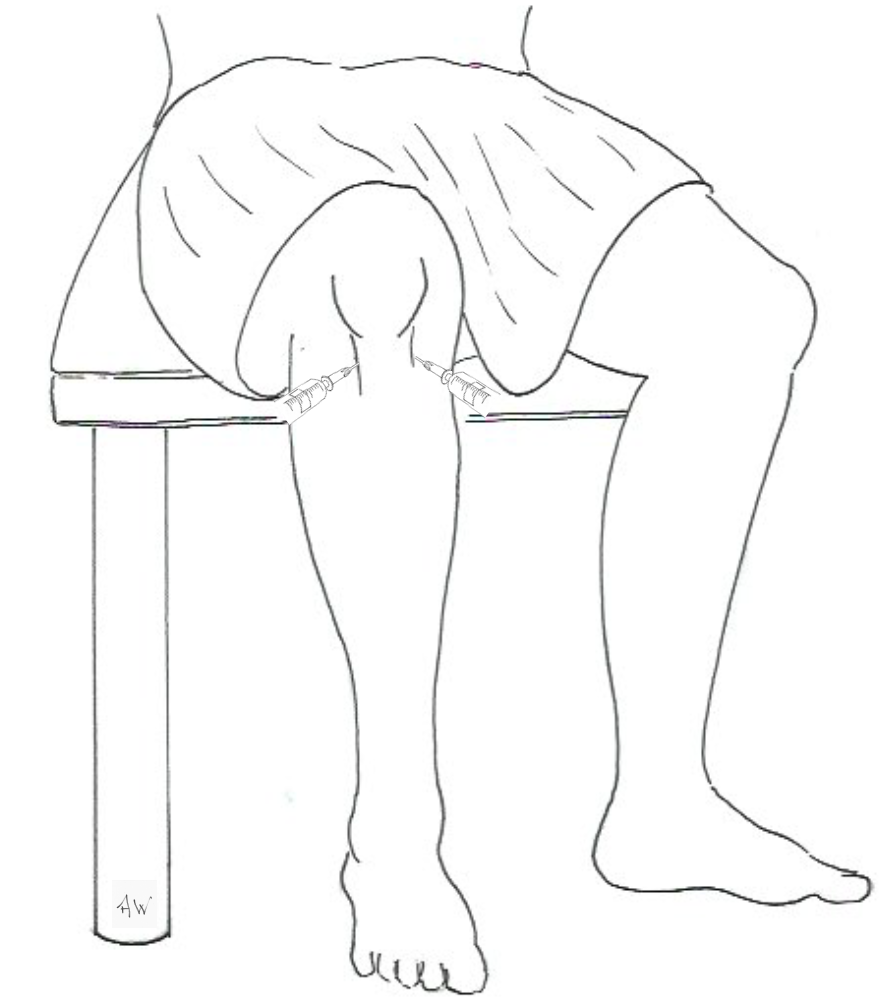
- the patient is sat on a couch with their lower leg hanging down
- the tibial plateau and patella tendon should be identified
- the needle can be inserted either laterally or medially to the patella tendon about a finger-tips breadth above the tibial plateau
- the needle is directed postero-medially when injecting laterally to the tendon or postero-laterally if injecting from a medial approach
Anterior approach to injection of knee joint - showing both medial and lateral approaches:
Anterior approach to knee joint injection - medial to patellar tendon
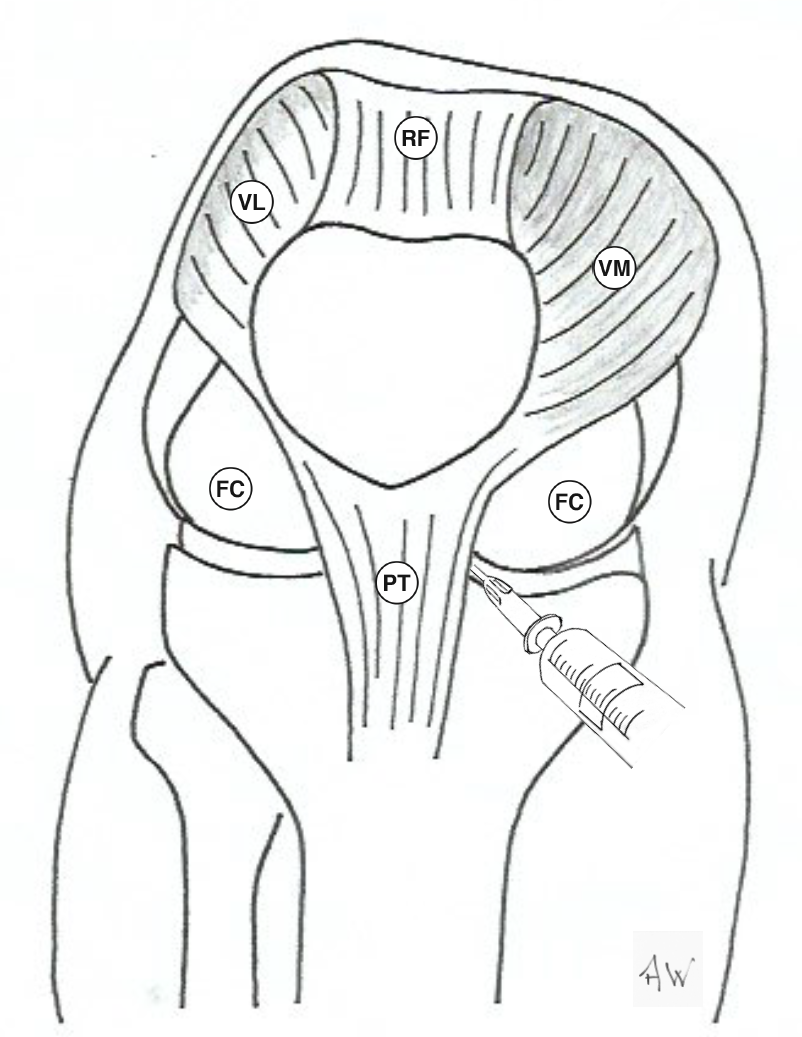
Anterior approach to knee injection - showing needle tip position
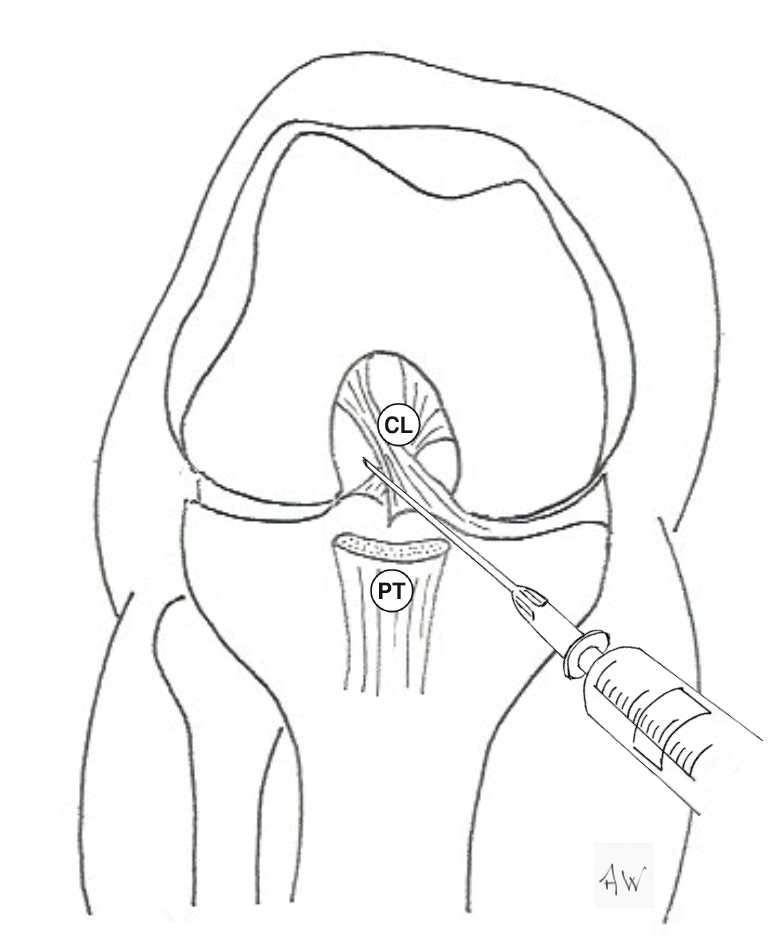
Anterior injection of the Knee Joint. View with medial femoral condyle removed:
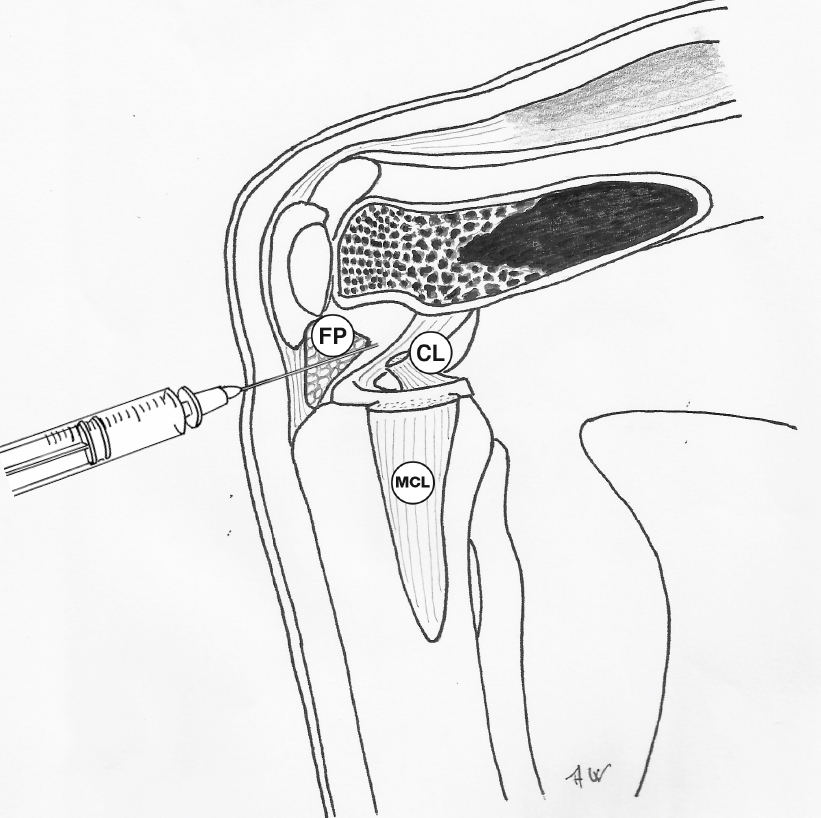
Key to acronyms:

Reference:
Related pages
Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.