History and examination
Gynaecomastia is asymptomatic in majority but occasionally there can be some irritation and some chafing of the breast and less commonly, patients may complain of tenderness (1).
The most important factor which should be focused during the clinical evaluation should be to determine whether gynaecomastia is the cause for the enlarged breast tissue or mass (2).
- in unilateral breast enlargement, a diagnosis other than gynaecomastia should be considered since gynaecomastia is usually bilateral (2,3)
It is important to obtain appropriate patient history and physical examination to exclude pseudogynecomastia (3).
- history should include:
- duration and course of symptoms
- history of sexual dysfunction
- presence of breast pain or tenderness
- detailed drug history - medications, indirect or environmental exposure to oestrogenic compounds, supplements, hormones, drugs of abuse including alcohol and marijuana, over the counter medication (including herbal products) etc.
- changes in virilization
- physical examination includes:
- breast examination - it is important to differentiate between
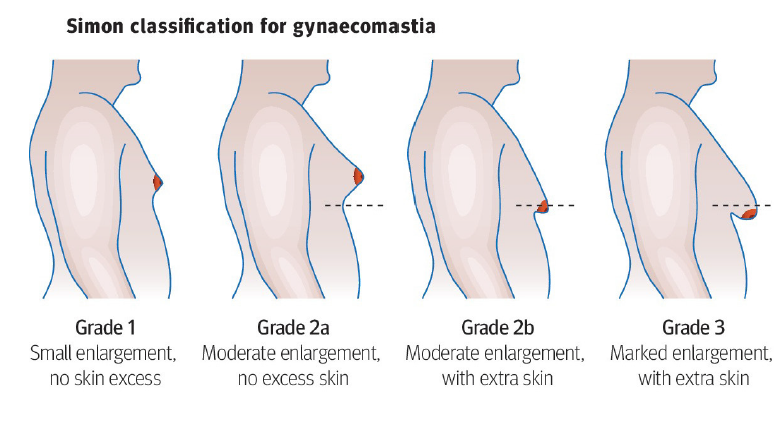
- gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia - the thumb and forefinger should be placed over the outer and inner breast margins and brought together in a pinching movement which will create a distinct disc of breast tissue under the nipple and areola tissue and if the diameter is under 2cm it is considered normal while a diameter of more than 2 cm is consistent with the gynaecomastia (1)
- gynecomastia and breast carcinoma
- signs of hyperthyroidism, chronic liver disease and hypogonadism, and include measurement of BMI
- testicular examination - to look for signs suggesting hypogonadism (small testicles) or testicular cancer (masses or abnormal consistency) (1).
- breast examination - it is important to differentiate between
Reference:
- (1) Porter K. The Basics - GP management of gynaecomastia. GP magazine 29 February 2012.
- (2) Braunstein GD. Clinical practice. Gynecomastia. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(12):1229-37.
- (3) Niewoehner CB, Schorer AE. Gynaecomastia and breast cancer in men. BMJ. 2008 Mar 29;336(7646):709-13.
- (4) Association of Breast Surgery Summary Statement (June 2019). Investigation and management of gynaecomastia in primary and secondary care.
Related pages
Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.