White cell count abnormal
The leukocytes are blood cells possessing a nucleus.
There are three key types - granulocytes, lymphocytes, monocytes::
- granulocytes
- a group of white blood cells defined on the basis of their granular appearance on microscopic examination after application of Romanowsky stains. They are all derived from a promyelocyte precursor within the bone marrow by granulopoiesis. Granulocytes include:
- neutrophils - polymorphonuclear leukocytes
- basophils
- eosinophils
- a group of white blood cells defined on the basis of their granular appearance on microscopic examination after application of Romanowsky stains. They are all derived from a promyelocyte precursor within the bone marrow by granulopoiesis. Granulocytes include:
- lymphocytes
- monocytes
They are involved in inflammatory and immune responses.
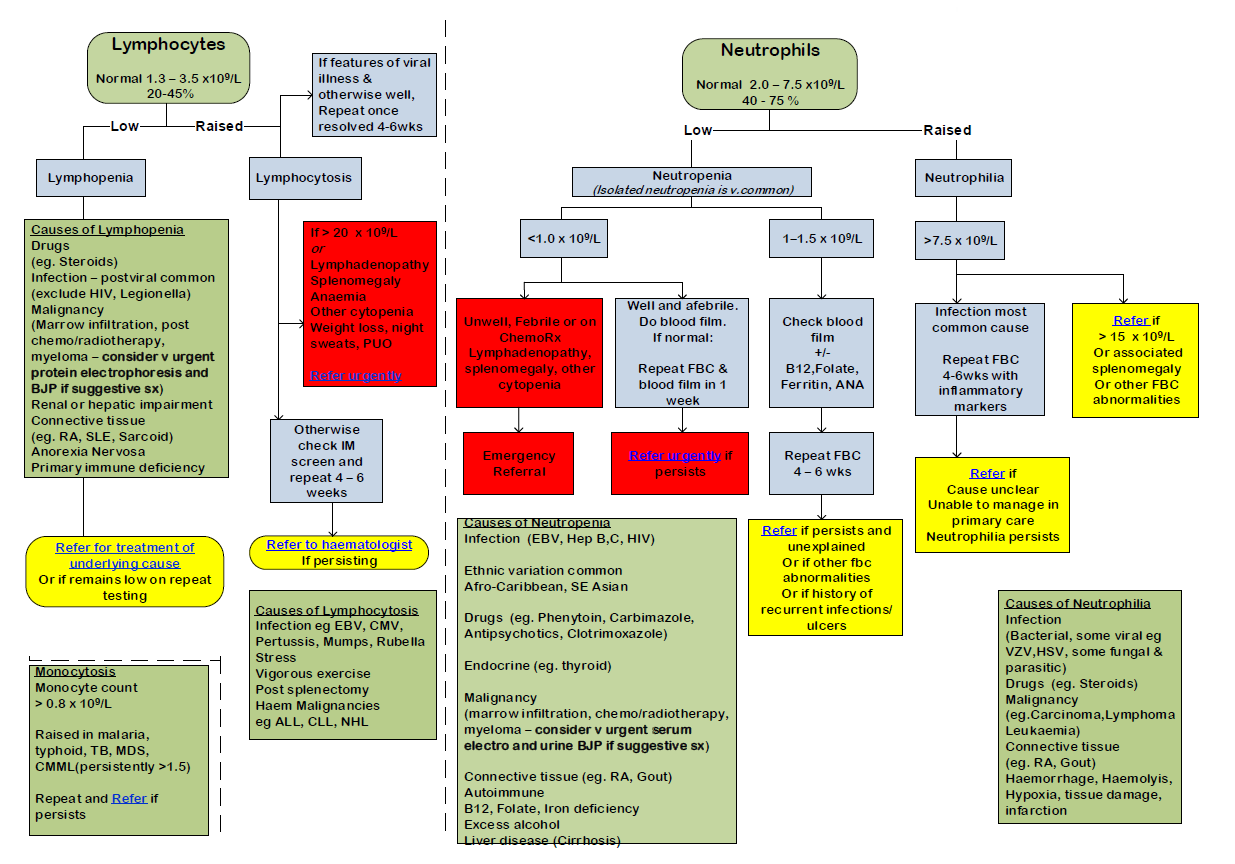
A schemata for managing raised neutrophils, lymphocytes or monocytes in adults is presented (1):
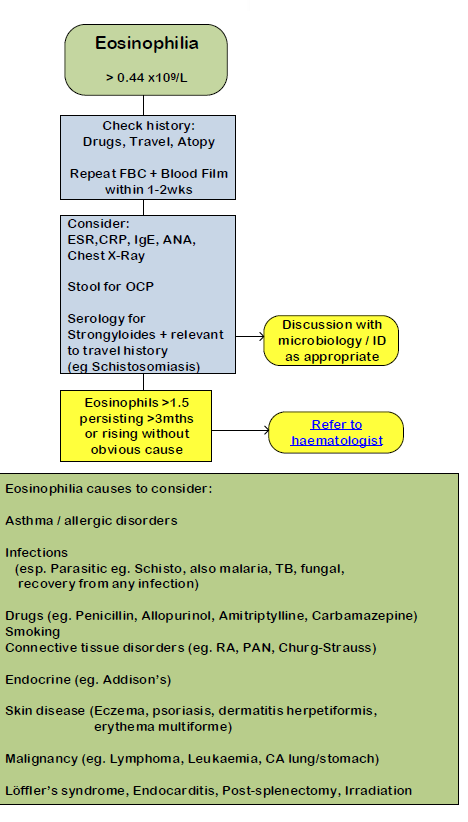
If raised eosinophil count in an adult (1):
Reference:
- NHS Camden CCG. Abnormal FBC guidance - for adults (Accessed 30/10/19)
Related pages
Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.