Treatment
Treatment of breast pain is directed at its cause.
Referred pain should be appropriately investigated and treated.
Pain originating from the chest wall may be treated with an injection of steroid and local anaesthetic into the painful area. This procedure often proves the diagnosis with rapid relief of the pain.
A firm support bra may give some relief.
A review concerning effectiveness of various treatments in management of mastalgia concluded that (1):
- topical NSAIDs are likely to be of benefit
- treatments where there is a trade off between benefits and harms
- danazol
- gestrinone
- gonadorelin analogues (luteinising hormone releasing hormone analogues)
- tamoxifen
- treatments of unknown effectiveness
- antibiotics
- dietary modifications (low fat, high carbohydrate)
- diuretics
- lisuride
- pyridoxine
- tibolone
- vitamin E
- the review concluded that bromocriptine, HRT (oestrogen), and progestogens were unlikely to be beneficial
- evening primrose oil was likely to be a harmful intervention
A suggested pathway is presented (3,4):
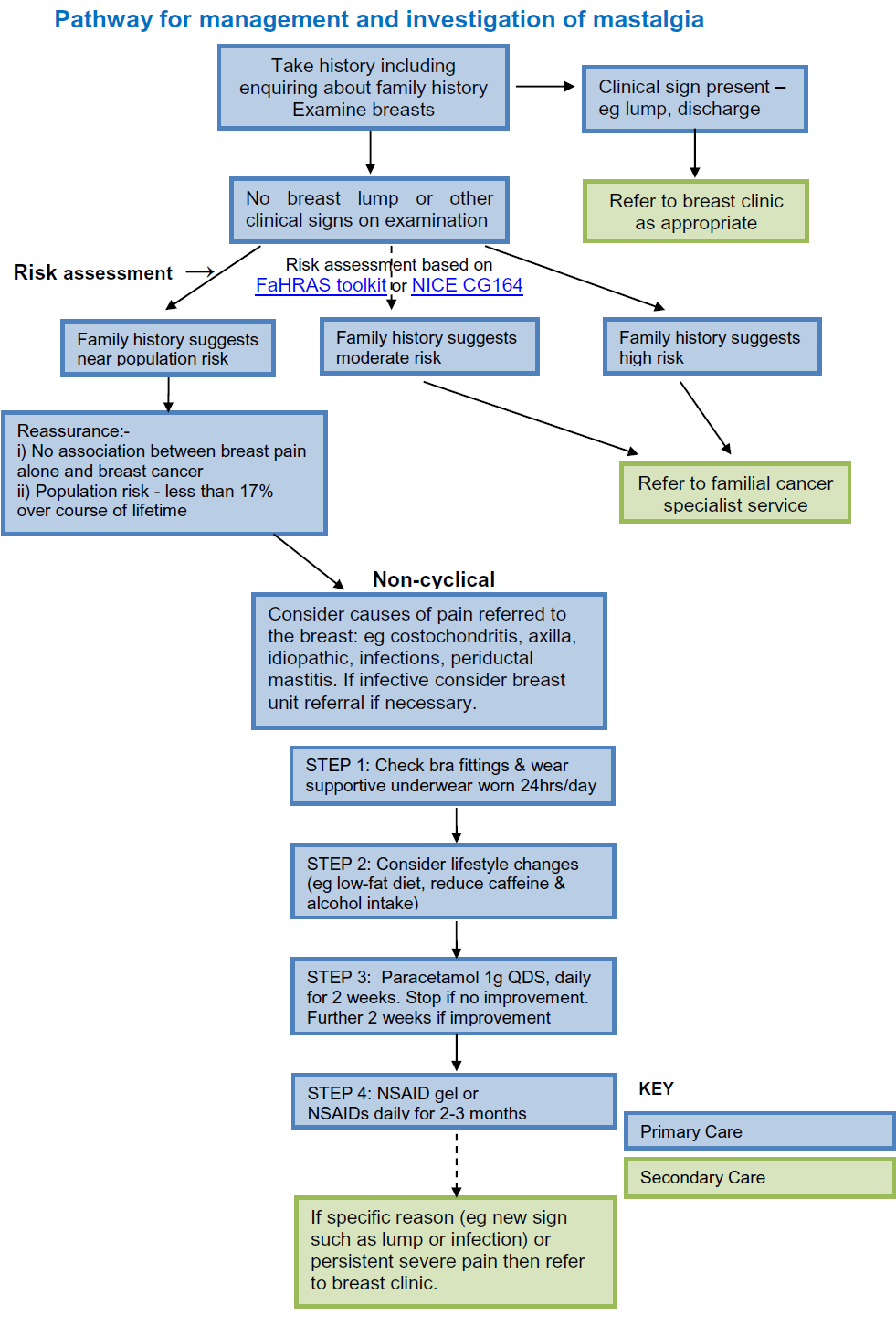
Reference:
- Clinical Evidence (September 2006). Breast pain.
- Colak T et al. Efficacy of topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in mastalgia treatment. J Am Coll Surg 2003;196:525-530.
- University Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust - Devon Breast Pain. Pathway for management and investigation of mastalgia (Accessed 5/3/2020)
- Goyal A. Breast Pain. BMJ Clin Evid. 2011; 2011: 0812
Related pages
Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.