BRCA1 and BRCA2 and pancreatic cancer
BRCA1/2 and pancreatic cancer
- Familial pancreatic cancer (FPC) includes those kindreds that contain at least two first degree relatives with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- has been suggested that about 10% of pancreatic cancer has a familial basis (1)
- has been suggested that about 10% of pancreatic cancer has a familial basis (1)
- BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene are well-known high-penetrant predisposing genes for hereditary breast and/or ovarian cancer (HBOC) (2)
- these genes are involved in the DNA damage response and DNA double-strand breaks repair
- pancreatic cancer is the third most common cancer associated with BRCA1/2 mutations, though the penetrance at age 70 is much lower (3)
- prevalence of BRCA2 mutations in pancreatic cancer patients is 1.4-8.2% for patients unselected for family history, about 6-16% among familal pancreatic cancer patients, and up to 17.2% in families with 3 or more pancreatic cancers (3)
- germline (inherited) mutations in the BRCA2 gene increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancer, and increase the risk of pancreatic cancer 3.5 to 10-fold
- while breast cancer develops in most families with a BRCA2 gene mutation, the absence of a breast cancer in a family should not be used to exclude germline BRCA2 mutations
- pancreatic cancer can run in BRCA2 gene mutation-carrying families without an apparent association with breast cancer
- germline BRCA2 mutations are particularly common in individuals of Ashkenazi Jewish heritage
- has been calculated that 1% of the Ashkenazi Jewish population carries a germline BRCA2 gene mutation, the 6174delT mutation, and these individuals, in addition to an increased risk of breast and ovarian cancer, have a 10-fold increased risk of developing pancreatic cancer (1)
- while breast cancer develops in most families with a BRCA2 gene mutation, the absence of a breast cancer in a family should not be used to exclude germline BRCA2 mutations
- germline (inherited) mutations in the BRCA2 gene increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancer, and increase the risk of pancreatic cancer 3.5 to 10-fold
- comparing to the general population, the risk of pancreatic cancer is about 2-6 fold in BRCA2 carriers and 2-5 fold in BRCA1 carriers (3)
- prevalence of BRCA2 mutations in pancreatic cancer patients is 1.4-8.2% for patients unselected for family history, about 6-16% among familal pancreatic cancer patients, and up to 17.2% in families with 3 or more pancreatic cancers (3)
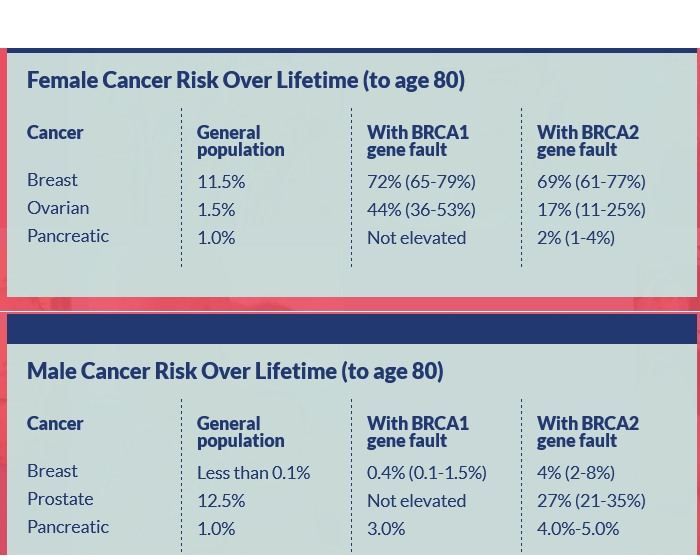
The NHS Jewish BRCA Testing Programme states the various cancers associated with BRCA1 and BRACA2:
Reference:
- Hruban RH, Canto MI, Goggins M, Schulick R, Klein AP. Update on familial pancreatic cancer. Adv Surg. 2010;44:293-311. doi:10.1016/j.yasu.2010.05.011
- Petersen GM. Familial pancreatic cancer. Semin Oncol. 2016;43(5):548-553. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2016.09.002
- Chen F, Roberts NJ, Klein AP. Inherited pancreatic cancer. Chin Clin Oncol. 2017;6(6):58. doi:10.21037/cco.2017.12.04
Related pages
Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.