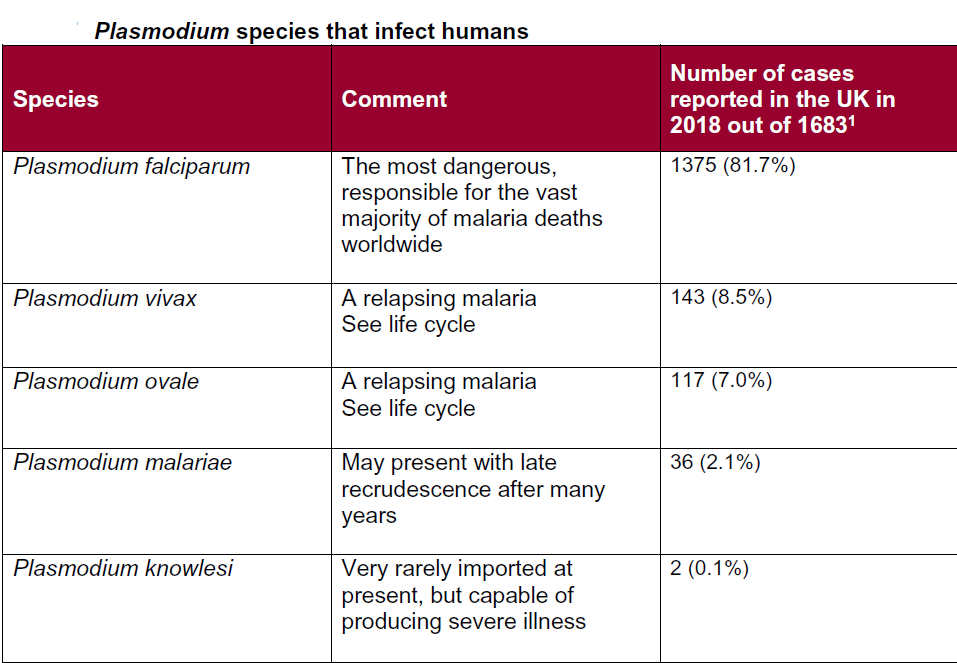
Malaria is a parasitic disease caused by genus Plasmodium. The parasite is spread by female Anopheles mosquitoes and five species of Plasmodium regularly infect humans:
- P. falciparum - most dangerous form, accountable for majority of deaths throughout the world
- P. ovale - a relapsing malaria
- P. vivax - a relapsing malaria
- P. malariae - least common type present in UK, may present with late recrudescence after many years
- Plasmodium knowlesi - very rarely imported at present, but capable of producing severe illness
Mixed infections with more than 1 species of malaria parasite are not commonly reported (14 in 2019) (3)
In recent years, the incidence of P. vivax in UK travellers has dropped, but in regions where it is a problem, the risk of acquiring vivax malaria is year round.
Plasmodium species that infect humans:
P. falciparum malaria is the most severe being characterised by paroxysms of chills, sweats and haemolysis. Cerebral malaria is a potentially fatal complication.
Protective factors against malaria include sickle cell trait; HLA-B53 positive (1).
Malaria may also be transmitted by blood transfusion and transplacentally. Another possible means of transmission is via so-called 'airport malaria' where infected mosquitoes have been transported by air.
Rarely malaria can occur in people without a travel history which is known as "cryptic" malaria (2).
Malaria is a statutorily notifiable disease in England and Wales (1).
It is not endemic in the UK (1,2)
Reference:
- (1) Public Health England. Guidelines for malaria prevention in travellers from the UK 2019
- (2) Health protection agency. Malaria
- (3) Public Health England. Guidelines for malaria prevention in travellers from the UK 2022
Related pages
Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.