Orf also known as contagious ecthyma is a rapidly growing zoonotic, mucocutaneous lesion caused by a pox virus. It is a condition generally seen in workers who have contact with sheep (1).
Workers handling infected animals (farmers, butchers, veterinarians, and shepherds), specially those who bottle-feed lambs in the spring, and those involved in shearing and slaughtering sheep are at an increased risk of acquiring the disease (1,2).
The disease is generally underreported since farmers familiar with the infection may not consult their GP’s. Two cases of orf were reported in 2006 and 2007 in Great Britain (2).
Clinical features include
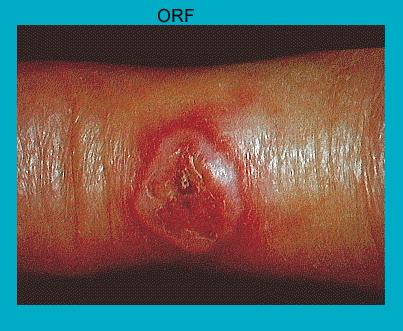
- small, firm, red papule(s) which develop rapidly one week after infection
- later these papules turn in to hemorrhagic and flat-topped lesions which may contain an umbilicated center (2)
- commonly seen on the fingers, hands, or forearms
- lesions can be extremely painful and might grow to a diameter of 5 cm, is often tender and may bleed easily (2)
- generally heals without scarring except the lesions complicated with secondary bacterial infections (1)
- associated features may include fever, lymphadenopathy and erythema multiforme.
Diagnosis is often clinical, laboratory evaluation using polymerase chain reaction testing may be necessary to differentiated from cutaneous anthrax since the appearance is similar in both the lesions (1).
Management:
- spontaneuous recovery occurs
- if secondary bacterial infection is a problem then antibiotics are required (2)
- preventive measures like barrier protection and hand washing can be used for people working with infected animals (1).
Reference
Related pages
Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.