UK's routine childhood immunisation programme (1)
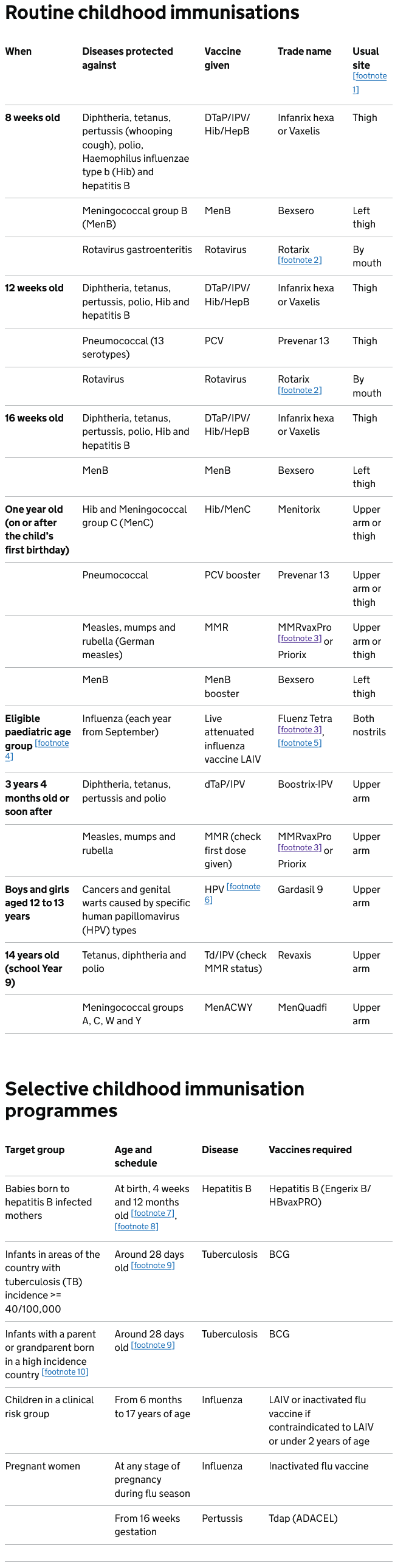
- intramuscular injection into deltoid muscle in upper arm or anterolateral aspect of the thigh
- rotavirus vaccine should only be given after checking for a severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) screening result
- contains porcine gelatine
- see annual flu letter (https://www.gov.uk/government/collections/annual-flu-programme)
- if LAIV (live attenuated influenza vaccine) is contraindicated or otherwise unsuitable use inactivated flu vaccine (check Green Book chapter 19 (https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/influenza-the-green-book-chapter-19) for details)
- see Green Book chapter 18a (https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/human-papillomavirus-hpv-the-green-book-chapter-18a) for immunising immunocompromised young people who will need 3 doses
- take blood for HBsAg at 12 months to exclude infection
- in addition hexavalent vaccine (Infanrix hexa or Vaxelis) is given at 8, 12 and 16 weeks
- check SCID screening outcome before giving BCG
- where the annual incidence of TB is >= 40/100,000 – see Tuberculosis by country: rates per 100,000 people (https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/tuberculosis-tb-by-country-rates-per-100000-people)
Reference:
- UK Health Security Agency. Routine childhood immunisations from 1 July 2024.
Related pages
- Immunisation
- Vaccines available
- Childhood immunisation schedule
- Types of immunisation
- General contraindications\guidelines to vaccination
- Diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus vaccination
- Measles, mumps and rubella vaccination
- Polio vaccination
- Hib vaccine
- Bacillus Calmette-Guerin vaccine
- GOBI-FFF
- Important groups to vaccinate
- Immunisations in pregnancy and breast feeding
- Vaccination for immunising individuals with asplenia, splenic dysfunction or complement disorders
Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.