Amniocentesis
Estimated that around 5% of the pregnant population (approximately 30,000 women per annum in the UK) are offered a choice of invasive prenatal diagnostic tests, most commonly amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS) (1)
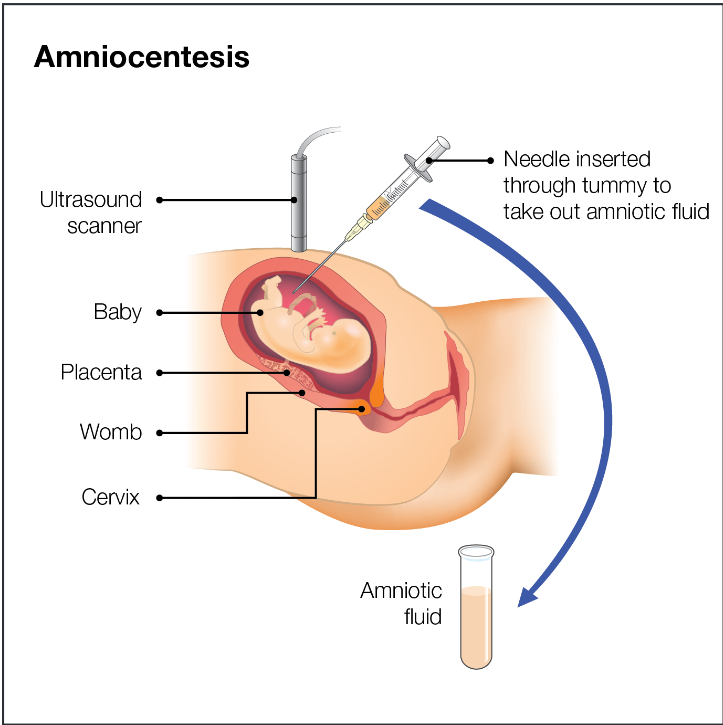
Amniocentesis is the most common invasive prenatal diagnostic procedure undertaken in the UK. Most amniocenteses are performed to obtain amniotic fluid for karyotyping from 15 weeks (15+0 ) onwards. Amniocentesis performed before 15 completed weeks of gestation is referred to as ‘early amniocentesis’.
This is the technique where, under ultrasound guidance, a needle is inserted into the amniotic sac through the abdominal wall. About 15-20mls of amniotic fluid removed. The fetal loss rate is 1%. The test is done anytime from 15 completed weeks.
- RCOG guidance states that (2):
- women should be informed that the additional risk of miscarriage following amniocentesis is around 1%
- women should be informed that the additional risk of miscarriage following CVS may be slightly higher than that of amniocentesis carried out after 15 weeks gestation
The cells in the fluid can then be cultured and karyotypically analysed for chromosomal abnormalities, for example, classically Down's syndrome.
More sophisticated analysis uses gene probes to detect genetic diseases - for example, cystic fibrosis. Inborn errors of metabolism can be diagnosed by assaying enzyme levels from the cultured amniotic fluid cells.
The process can be used to detect male offspring in families known to carry an X-linked disease, for example, Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
The technique can also be used to measure protein levels in the amniotic fluid - for example, AFP and acetyl- cholinesterase in suspected cases of neural tube defects. 17-alpha-hydroxyprogesterone levels can be measured in suspected cases of adrenogenital syndrome.
Timing of results from amniocentesis varies:
- 2-3 weeks for a karyotype
- 3 working days for rapid test such as QF PCR (quantitative fluorescence polymerase chain reaction) - in this test small sections (markers) of DNA from the sample are amplified, labelled with fluorescent tags and the amounts measured by electrophoresis - this test checks for genetic conditions such as trisomies 18, 13 and 21
Up to 1.5% of samples are unsatisfactory because the cells fail to grow or the sample was contaminated with blood.
Notes (1):
- PHE states that 1 in 200 women will miscarry following a CVS or amniocentesis
- up to 6 in 100 women (6%) will be offered a second procedure because it is not always possible to get a result from the first CVS or amniocentesis.
Reference:
- PHE Blog - CVS and aminocentesis leaflet updated and published in HTML (28/2/2020)
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (UK). Green Top guideine - number 8 - Amniocentesis and Chorionic Villus Sampling
Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.