Management of acute otitis media in primary care
Acute otitis media is an acute inflammation of the middle ear cleft which includes the eustachian tube and the mastoid cavity. It is extremely common in children, but can occur at any age. The condition ranges from a mild inflammation to the formation of frank pus.
Management of otitis media includes (1):
- discussion and reassurance about the natural course of the illness
- in children, 80% recover in around three days without antibiotics
- complications are rare
- pain relief
- paracetamol and ibuprofen have been shown to reduce earache
- decongestants or antihistamines
- insufficient evidence to support the use of decongestants or antihistamines.
- consider antibiotics
- antibiotics should not be prescribed routinely for acute otitis media in children. They reduce pain to a small degree but this should be balanced against the risk of causing adverse effects such as vomiting, diarrhoea or rashes
- antibiotics may be beneficial in sub-groups of patients. For example, children:
- under two years with bilateral infection or
- with discharge from the ear or
- who are systemically unwell (e.g. fever or vomiting) or
- with recurrent infections
- Public Health England guidance suggests (2):
- regular paracetamol or ibuprofen for pain (right dose for age or weight at the right time and maximum doses for severe pain)
- criteria for antibiotic use:
- if otorrhoea or under 2 years with infection in both ears
- then consider no antibiotic, back-up antibiotic or immediate antibiotic
- if no otorrhoea or under 2 years with infection in one ear or 2 years or older with ear infection (in one or both ears)
- then consider no antibiotic or back-up antibiotic
- if systemically very unwell or high risk of complications
- requires immediate antibiotic
- if otorrhoea or under 2 years with infection in both ears
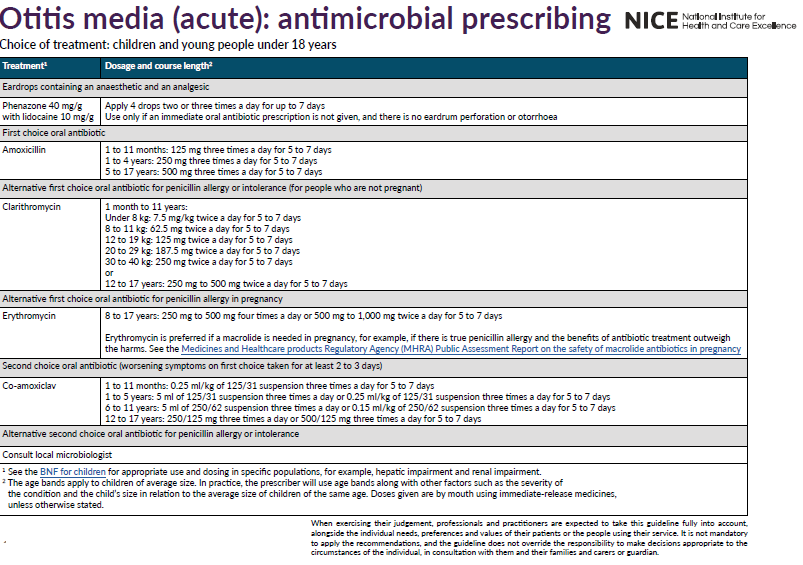
- choice of antibiotic:
- First choice: amoxicillin for 5 to 7 days
- Penicillin allergy: clarithromycin for 5 to 7 days (but erythromycin is preferred if pregnant)
- Second choice: co-amoxiclav
NICE suggest an algorithm of (3):
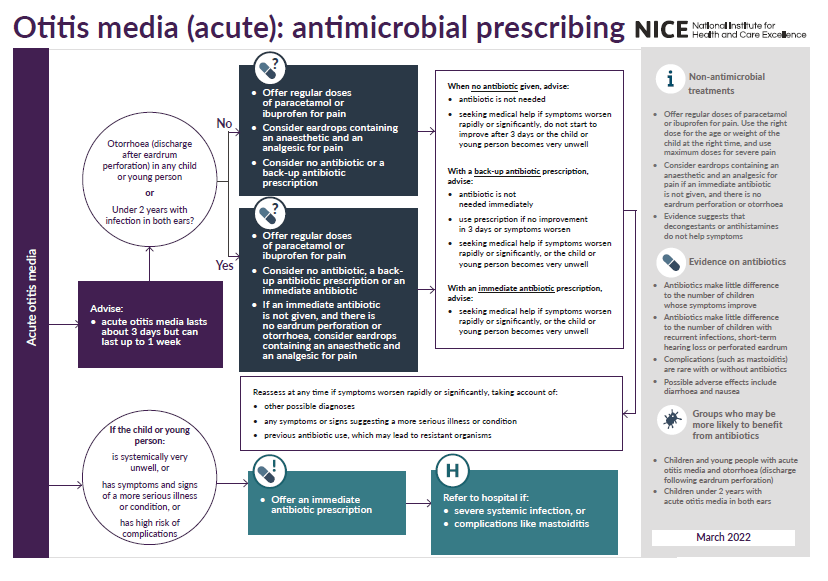
Antibiotics for otitis media (3):
If acute otitis media persists despite adequate antibiotic therapy then very rarely a myringotomy (tympanostomy) may be necessary (1)
- this surgical procedure is carried out under general anaesthetic
- a large incision is made in the tympanic membrane and the ear is allowed to drain
- the ear will discharge following the myringotomy.
- the outer meatus should be wiped regularly
- complications of tympanostomy include (1):
- transient and persistent otorrhea
- tympanosclerosis
- atrophy
- perforation of the tympanic membrane
- cholesteatoma
Reference:
- Marchisio P, Galli L, Bortone B, et al; Updated Guidelines for the Management of Acute Otitis Media in Children by the Italian Society of Pediatrics: Treatment. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2019 Dec;38(12S Suppl):S10-S21.
- Public Health England (June 2021). Managing common infections: guidance for primary care
- NICE (March 2022). Otitis media (acute): antimicrobial prescribing
Related pages
Create an account to add page annotations
Add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation, such as a web address or phone number. This information will always be displayed when you visit this page