Raised WCC (neutrophil)
Neutrophils comprise approximately 40% to 60% of the total leukocyte count. Neutrophilia, an increased neutrophil count at least 2 standard deviations above the mean or >7700 neutrophils/µL in adults, is the most common cause of leucocytosis. (1)
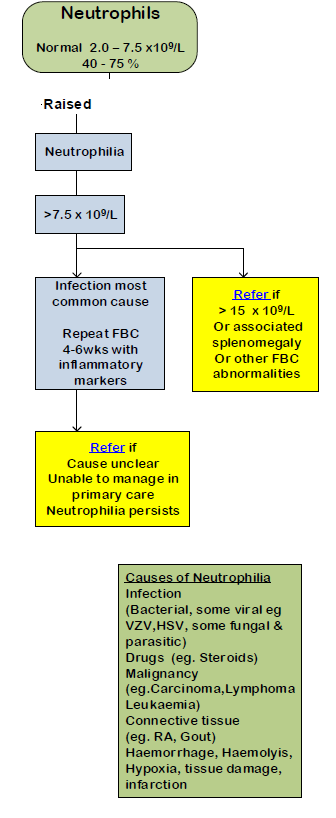
Neutrophils > 7.5 x 109/l may be caused by:
- bacterial infection
- surgery
- burns
- trauma
- haemorrhage
- infarction
- inflammation
- polymyalgia
- myeloproliferative disorders
- leukaemias
- polyarteritis nodosa
- drugs e.g. steroids
A suggested management of raised neutrophils in adults is:
Reference
- Riley LK, Rupert J. Evaluation of Patients with Leukocytosis. Am Fam Physician. 2015 Dec 01;92(11):1004-11
Related pages
Create an account to add page annotations
Add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation, such as a web address or phone number. This information will always be displayed when you visit this page