Childhood immunisation schedule
The vaccines that children and adults should receive are included in the tables below,
The Complete UK Immunisation Schedule:
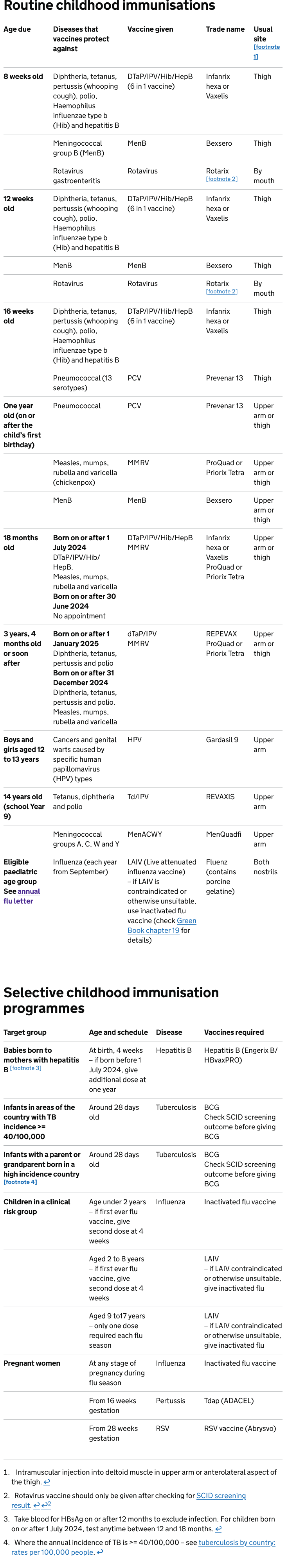
Reference:
- UK Health Security Agency (December 5th 2025). Routine childhood immunisation schedule from 1 January 2026.
Related pages
- Meningococcal vaccination
- Immunisations in children
- Prematurity and immunisation
- HPV vaccine
- Bacillus Calmette-Guerin vaccine
- Vaccination for immunising individuals with asplenia, splenic dysfunction or complement disorders
- Vaccination of individuals with uncertain (unknown) or incomplete immunisation status
- Using paracetamol to prevent and treat fever after MenB vaccination
Create an account to add page annotations
Add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation, such as a web address or phone number. This information will always be displayed when you visit this page