HBsAg serocoversion
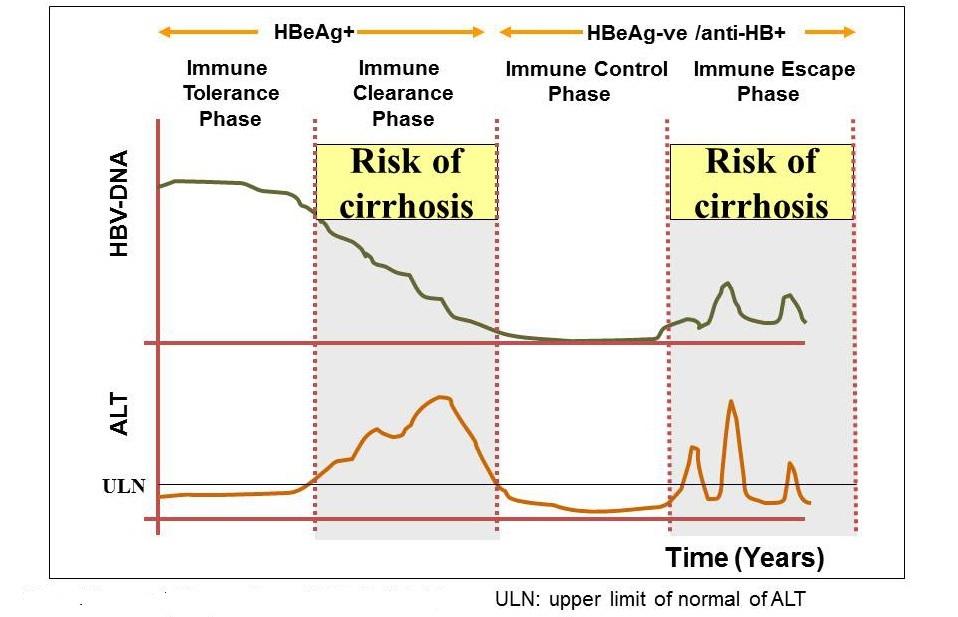
The natural history of CHB is dynamic and complex, and progresses nonlinearly through several recognizable phases. The phases are of variable duration, are not necessarily sequential, and do not always relate directly to criteria and indications for antiviral therapy (1,2).
phase | HBeAg serological status | pattern | indications for treatment |
1. “Immune tolerant” | HBeAg positive |
| treatment not generally indicated, but monitoring required |
2. “Immune active” (HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis) | HBeAg positive; may develop anti-HBe |
| treatment may be indicated |
3. Inactive chronic hepatitis “Immune control” (previously called inactive carrier) | HBeAg negative, anti-HBe positive |
| treatment not generally indicated, but monitoring required for reactivation and HCC |
4. “Immune escape” (HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis) | HBeAg negative, with or without being anti-HBe positive |
|
|
5.“Reactivation” or “acute-onchronic hepatitis” | HBeAg positive or negative |
| treatment indicated |
Reference:
Related pages
Create an account to add page annotations
Add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation, such as a web address or phone number. This information will always be displayed when you visit this page