Classification of statin related muscle (SRM) toxicity
- Classification of statin related muscle toxicity (SRM)
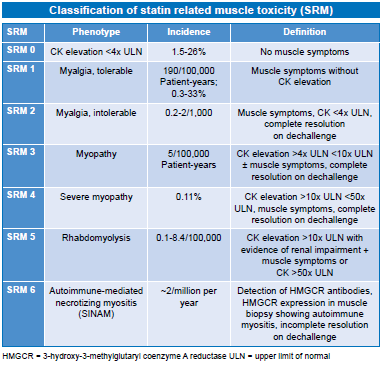
- SRM is a spectrum from myalgia to severe myopathy
- SRM 0 - does not preclude statin therapy, consider reducing starting dose
- SRM 1-3 manage according to pathway
- When SRM4 is suspected, without evidence of impaired renal function, discontinue statin therapy immediately and refer for outpatient assessment. Assess and treat possible contributory factors and re-assess the need for a statin. Intensify lifestyle modifications and consider alternative lipid lowering regimens.
- If rhabdomyolysis (SRM5) is suspected, immediately stop statins, urgently refer to inpatient assessment and management including intravenous rehydration as required to preserve renal function. Do not wait for measurement of urinary myoglobin. Post recovery, manage as for SRM4
- Statin induced necrotizing autoimmune myositis (SINAM) (SRM6) should be suspected in patients with progressive muscle weakness and ongoing CK elevation despite statin withdrawal. Requires immunosuppressive treatment and avoidance of re-exposure to statins. Re-assess the need for lipid lowering therapy - may be eligible for treatment with PCSK9 inhibitor (NICE TA 393, 394)

Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.