Oral contraceptive pill (risk factors for arterial disease)
- a combined pill containing a low dose of oestrogen (i.e. 30 mcg) is indicated in women who have migraines without auras - this is because the risk of stroke is greater the higher the dose of oestrogen in the combined pill
- a DTB review (1) suggested that low-dose pill can also be given to women who have migraines without auras but have one additional risk factor for stroke - however the review emphasises that these patients must be followed up carefully
- prescribing decisions, with respect to combined hormonal contraception, are made based on the UKMEC criteria below which define migraine with an aura as an absolute contraindication to combined hormonal contraception - see below for further details and guidance with respect to different migraine scenarios
UKMEC Criteria state:
Cardiovascular factors (including migraine) and UKMEC categories (3):
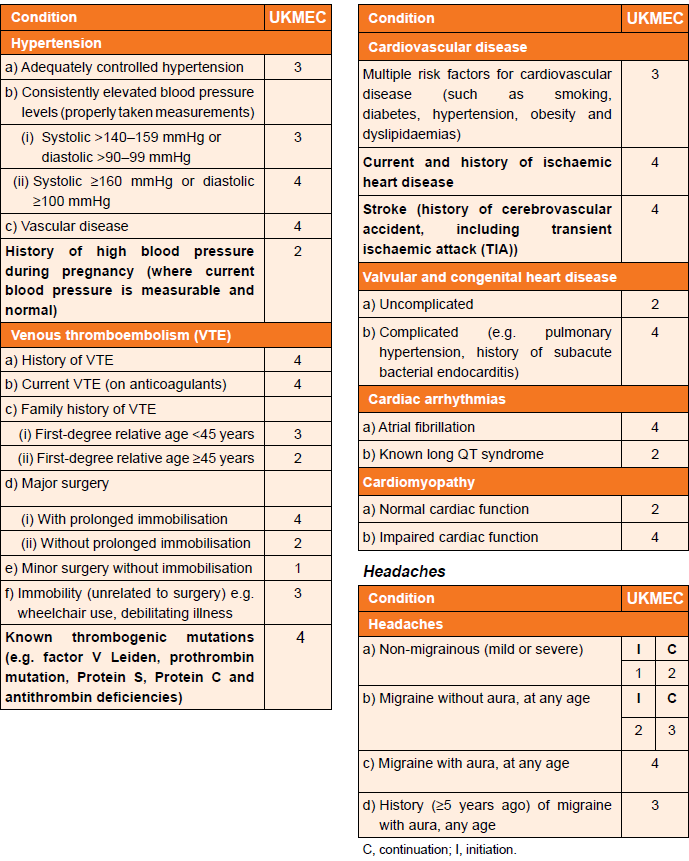
In consideration of UKMEC criteria and combined hormonal contraception (CHC):

Check the summary of product characteristics before prescribing any combined oral contraceptive pill.
Reference:
- Drug and Therapeutics Bulletin (2000), 38 (1), 1-4.
- British National Formulary. Oral contraceptives.
- FSRH Clinical Guidance: Combined Hormonal Contraception; Faculty of Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare (January 2019 - amended October 2023)
Related pages
- Migraine and the combined oral contraceptive pill
- Combined oral contraceptive pill
- Oral contraceptives and smoking
- Oral contraceptives and hypertension
- Obesity and combined oral contraceptive
- UKMEC (UK Medical Eligibility for Contraceptive Use) criteria
- General contraindications to combined oral hormonal contraceptive
Create an account to add page annotations
Add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation, such as a web address or phone number. This information will always be displayed when you visit this page