Diabetes mellitus and hypertension
The guidance regarding the diagnosis of systemic hypertension has been updated to (1):
Confirm a diagnosis of hypertension in people with a clinic blood pressure of 140/90 mmHg or higher and ABPM daytime average or HBPM average of 135/85 mmHg or higher.
If blood pressure measured in the clinic is 140/90 mmHg or higher, take a second measurement during the consultation. If the second measurement is substantially different from the first, take a third measurement. Record the lower of the last 2 measurements as the clinic blood pressure.
If clinic blood pressure is between 140/90 mmHg and 180/120 mmHg, offer ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) to confirm the diagnosis of hypertension.
When using ABPM to confirm a diagnosis of hypertension, ensure that at least 2 measurements per hour are taken during the person's usual waking hours (for example, between 08:00 and 22:00). Use the average value of at least 14 measurements taken during the person's usual waking hours to confirm a diagnosis of hypertension.
BP targets in adults:
in people with CKD and diabetes, and also in people with an ACR of 70 mg/mmol or more, aim to keep the systolic blood pressure below 130 mmHg (target range 120-129 mmHg) and the diastolic blood pressure below 80 mmHg
Starting antihypertensive drug treatment
Offer antihypertensive drug treatment in addition to lifestyle advice to adults of any age with persistent stage 2 hypertension. Use clinical judgement for people of any age with frailty or multi-morbidity.
Discuss starting antihypertensive drug treatment, in addition to lifestyle advice, with adults aged under 80 with persistent stage 1 hypertension who have 1 or more of the following:
- target organ damage
- established cardiovascular disease
- renal disease
- diabetes
- an estimated 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease of 10% or more
- use clinical judgement for people with frailty or multi-morbidity
Consider antihypertensive drug treatment in addition to lifestyle advice for adults aged under 60 with stage 1 hypertension and an estimated 10-year risk below 10%
- note that 10-year cardiovascular risk may underestimate the lifetime probability of developing cardiovascular disease
Consider antihypertensive drug treatment in addition to lifestyle advice for people aged over 80 with a clinic blood pressure of over 150/90 mmHg
- use clinical judgement for people with frailty or multi-morbidity
Measure standing as well as seated blood pressure in people with hypertension and:
- with type 2 diabetes or
- with symptoms of postural hypotension or
- aged 80 and over.
- in people with a significant postural drop or symptoms of postural hypotension, treat to a blood pressure target based on standing blood pressure
Offer people with isolated systolic hypertension (systolic blood pressure 160 mmHg or more) the same treatment as people with both raised systolic and diastolic blood pressure
For adults aged under 40 with hypertension, consider seeking specialist evaluation of secondary causes of hypertension and a more detailed assessment of the long-term balance of treatment benefit and risks
Suggested management for patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension (1):
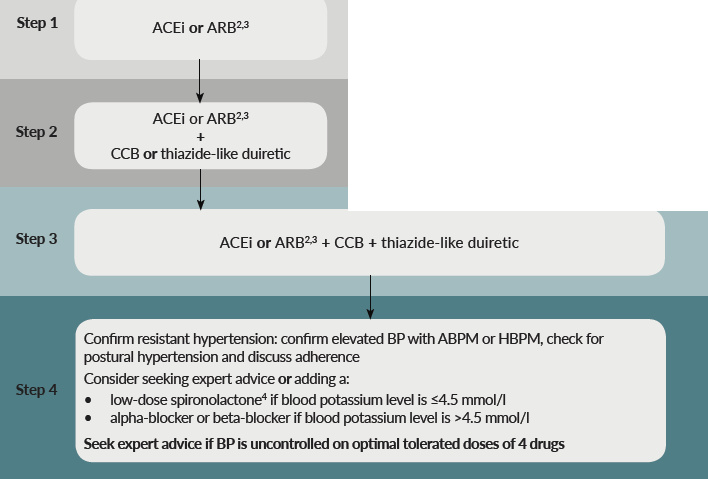
- For women considering pregnancy or who are pregnant or breastfeeding, see NICE's guideline on hypertension in pregnancy. For people with chronic kidney disease, see NICE's guideline on chronic kidney disease. For people with heart failure, see NICE's guideline on chronic heart failure
- See MHRA drug safety updates on ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II receptor antagonists: not for use in pregnancy, which states 'Use in women who are planning pregnancy should be avoided unless absolutely necessary, in which case the potential risks and benefits should be discussed', ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists: use during breastfeeding and clarification: ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists. See also NICE's guideline on hypertension in pregnancy.
- Consider an ARB, in preference to an ACE inhibitor in adults of African and Caribbean family origin.
Abbreviations: ABPM, ambulatory blood pressure monitoring; ACEi, ACE inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin-II receptor blocker; BP, blood pressure; CCB, calcium-channel blocker; HBPM, home blood pressure monitoring.
NICE guidance states with respect to type 1 diabetes (2):
Blood pressure management
- intervention levels for recommending blood pressure management should be 135/85 mmHg unless the adult with type 1 diabetes has albuminuria or 2 or more features of metabolic syndrome, in which case it should be 130/80 mmHg
- start a trial of a renin-angiotensin system blocking drug as first-line therapy for hypertension in adults with type 1 diabetes
Do not allow concerns over potential side effects to inhibit advising and offering the necessary use of any class of drugs, unless the side effects become symptomatic or otherwise clinically significant. In particular:
- do not avoid selective beta-adrenergic blockers where indicated in adults on insulin
- low-dose thiazides may be combined with beta-blockers
- when calcium channel antagonists are prescribed, use only long-acting preparations
- use direct questioning to detect the potential side effects of erectile dysfunction, lethargy and orthostatic hypotension with different drug classes
Reference:
- NICE. Hypertension in adults: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline NG136. Published August 2019, last updated November 2023
- NICE. Type 1 diabetes in adults: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline NG17. Published August 2015, last updated August 2022.
Related pages
- Measuring blood pressure
- Management of hypertension in diabetics
- Hypertension (target blood pressure in diabetics)
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study
- Systemic hypertension
- Aspirin in hypertensive patients
- Diabetes mellitus
- UKPDS - hypertension in type 2 diabetes
- Diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease risk
- ACE inhibitors in diabetes
- ADVANCE study (combination of an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) and a diuretic on macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus)
- Hypertension (target blood pressure in Type II diabetes)
- Number need to treat (NNT) to prevent cardiovascular event if diabetes and hypertension
- Hypertension and risk of development of type 2 diabetes
Create an account to add page annotations
Annotations allow you to add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation. E.g. a website or number. This information will always show when you visit this page.